Sie befinden sich hier
Inhalt
RNAi Screening
We develop and apply high-throughput screening technologies to systematically survey the Drosophila genome for new functions. Our work focuses on automated RNA interference (RNAi) screenings to identify novel targets in cellular processes.
RNA Interference
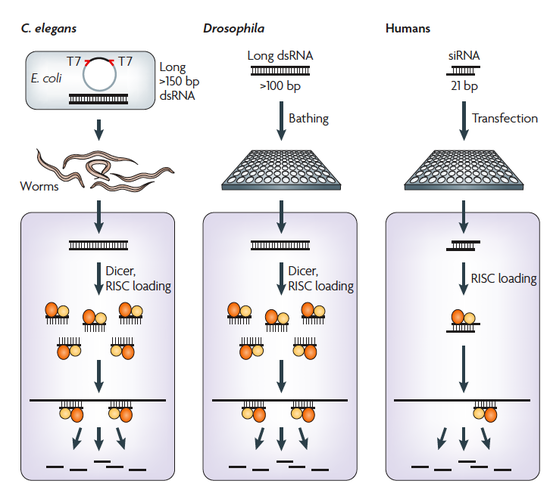
RNA interference (RNAi) has emerged as a powerful tool to systematically dissect gene function by depleting transcripts through the introduction of homologous short or long double-stranded RNAs. Discovered in C. elegans and plants, RNAi is now also widely employed for gene-silencing studies in many model systems, including Drosophila and human cells. With the development and availability of genome-wide RNAi libraries in combination with high-throughput screening techniques, RNAi can be used to query genomes for a variety of cell or organism-based phenotypes.
RNAi screening in Drosophila cells
RNAi in cultured Drosophila cells can be triggered by adding in vitro generated double-stranded RNAs to the cell culture medium. Compared to screens in mammalian cells, Drosophila has the key advantages of relatively low genetic redundancy and high efficacy of RNAi reagents. Using this model organism our group was able to identify a number of new factors of Wnt, JAK/STAT, IMD and further conserved signaling pathways.
Screening experiments can be performed genome-wide or for a small number of genes, for example those in specific functional groups. With cell-based assays we can measure a diverse set of phenotypes, ranging from homogenous cell viability readouts over alterations in reporter gene expression to high-content assays using automated microscopy.
RNAi Screening Resources
Our group has long-standing experience in cell-based RNAi screening in Drosophila. We constantly develop and optimize screening reagents and methods. We developed and generated a novel genome-wide Drosophila RNAi library with an optimized design. Several genome-wide RNAi screens have been conducted so far using the second-generation library (Heidelberg 2).
This library recently served to generate a genome-wide in vivo RNAi Drosophila library (VDRC KK library), enabling to perform cell-based and in vivo studies using the same RNAi constructs. The library is constantly updated according to new gene annotations and further developed in terms of specificity and efficiency.
Drosophila RNAi libraries (HFA and BKN)
Heidelberg 1 (HFA)
This library is the original Drosophila library containing the HFA amplicons as templates that were generated by Renato Paro's laboratory. The library has been largely replaced by newer designs. Complete sequence information can be obtained from Boutros et al. (2004). Genome-wide RNAi analysis of growth and viability in Drosophila cells. Science, 303(5659):832-5 (PubMed) or by browsing the GenomeRNAi database.
Heidelberg 2 (BKN)
The library has been completely redesigned using the software Next-RNAi (Horn et al. (2010). Design and evaluation of genome-wide libraries for RNAi screens. Genome Biol. 11(6):R61, PubMed). The constructs have been optimized to exclude low complexity regions and other sequence motifs that induce off-target effects. The library contains all BKN amplicons and is available in different formats:
- Genome-wide library
- Kinase library containing three amplicons against all kinases in the Drosophila genome
- Phosphatase library
- Transcription factor library
- C. elegans negative control library
- Proteasome library
- E3 ligase library
- Peptidase library
Complete sequence information can be obtained also by browsing the GenomeRNAi database.
Methods for RNAi screening in Drosophila cells
Methods for RNAi screening in Drosophila cells
The Department develops and applies technologies for high-throughput RNAi screening in Drosophila cells. Particular areas of interests are new pathway-specific cell-based assays for cancer-relevant signaling systems to identify new targets. Futhermore we establish new automation protocols to miniaturize cell-based assays and new detection modes, such as highly parallel imaging and image analysis. In this context, automated microscopy enables the multiparametric analysis of phenotypes. We routinely apply different kinds of luminescence- and fluorescence-based assays to measure cell viability, reporter activity and cell morphology.
Computational Tools
We developed a number of computational tools for the design and analysis of high-throughput screening experiments. These include software tools to design and evaluate RNAi reagents (E-RNAi, NEXT-RNAi), a user-friendly tool for statistical analysis of screening data and a comprehensive database for RNAi phenotypes.
web cellHTS2
web-based implementation of cellHTS2 for the statistical analysis of screening experiments
High-throughput screens by RNAi generate large primary data sets which need to be analyzed and annotated to identify phenotypic hits. The web application, a front-end to the Bioconductor/R package cellHTS2, guides the user through all configuration steps required for analysis of single or multi-channel experiments. The web-application provides various options for standardization and normalization methods, annotation of data sets and a comprehensive HTML report of the screening data analysis, including a ranked hit list. Sessions can be saved and re-stored for later re-analysis.
Reference: Pelz et al. (2010). web cellHTS2: a web-application for the analysis of high-throughput screening data. BMC Bioinformatics. 11:185. (PubMed)
Genome-RNAi
Comprehensive database for RNAi phenotypes from Drosophila and human screens
The GenomeRNAi database contains phenotypes from published RNA interference (RNAi) screens in Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens. The database connects observed phenotypes with annotations of targeted genes and information about the RNAi reagent used for the perturbation experiment. The availability of phenotypes from Drosophila and human screens also allows for phenotype searches across species. Besides reporting quantitative data from genome-scale screens, GenomeRNAi also enables reporting of data from microscopy experiments and curated phenotypes from published screens. In addition, the database provides an updated resource of RNAi reagents and their predicted quality that are available for the Drosophila and the human genome.
Reference: Gilsdorf et al. (2010). GenomeRNAi: a database for cell-based RNAi phenotypes. 2009 update. Nucleic Acids Res., 38(Database issue):D448-52. (PubMed)
E-RNAi
Web-based tool for the design of RNAi constructs
For the correct assessment of phenotypes, a key issue remains the stringent quality control of long double-stranded RNAs (dsRNA) to calculate potential off-target effects that may obscure the phenotypic data. We have developed a web-based tool to evaluate and design optimized dsRNA constructs.
Reference: Horn T. and Boutros M. (2010). E-RNAi: a web application for the multi-species design of RNAi reagents – 2010 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 38(Web Server issue):W332-9. (PubMed)
NEXT-RNAi
Software for the design and evaluation of genome-wide RNAi libraries
NEXT-RNAi is a software for the design and evaluation of genome-wide RNAi libraries and performs all steps from the prediction of specific and efficient RNAi target sites to the visualization of designed reagents in their genomic context. The software enables the design and evaluation of siRNAs and long dsRNAs and was implemented in an organism-independent manner allowing designs for all sequenced and annotated genomes. It requires the minimal input of desired target sequences and an off-target database. NEXT-RNAi implements several methods to predict a reagents' quality and offers many special features such as the straight-forward design of independent RNAi reagents.
Reference: Horn et al. (2010). Design and evaluation of genome-wide libraries for RNAi screens. Genome Biol. 11(6):R61. (PubMed)
Enquiries about RNAi reagents and screening
The second-generation Drosophila dsRNA library (Heidelberg 2) can be obtained from us in a pre-aliquoted ready-to-use form. We provide whole-genome RNAi libraries, sub-libraries or custom-made sets for selected targets. Please contact us for costs and further information.
If you are interested in performing a screen with us, we would need to know certain information to determine whether we can perform such a screening experiment in collaboration. Most high-throughput screens have specific requirements with regards to assay development and screening setup.
The form below helps us to understand the biological background of the screen and the technical requirement. Please email the form to ulrike.hardeland@medma.uni-heidelberg.de. Please feel free to contact us and to discuss your screening idea.
Contact
Department Head
Prof. Dr. Michael Boutros
Phone: +49 (0)621/383-9650
michael.boutros@medma.uni-heidelberg.de
Project Management
Dr. Ulrike Hardeland
Phone: +49 (0)621/383-9648
ulrike.hardeland@medma.uni-heidelberg.de