You are here
Content

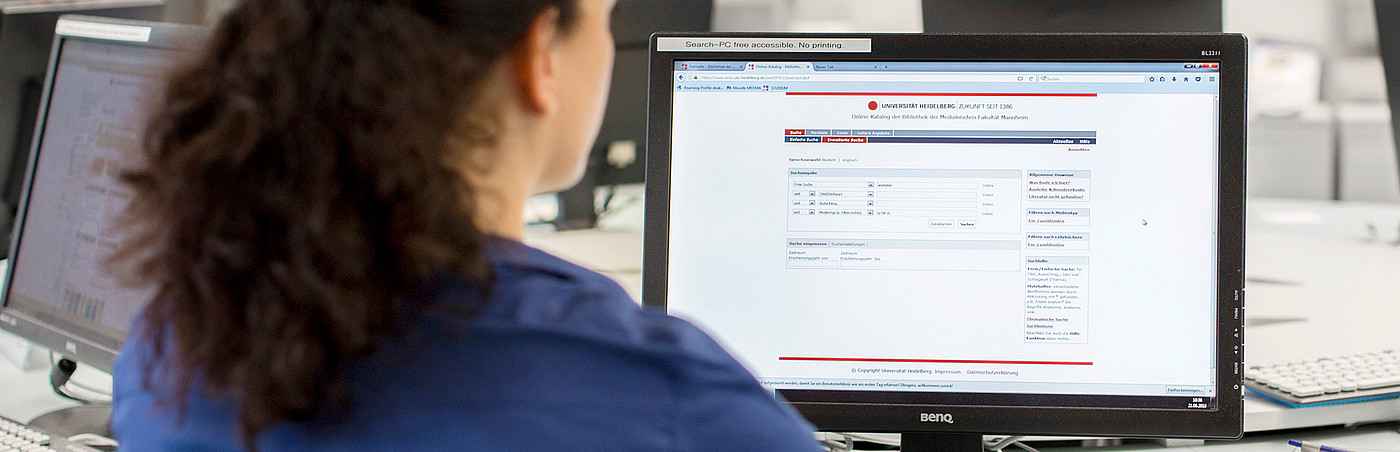
The licensed article database Embase (comparable to PubMed) evaluates international (primarily English-language) biomedical journals. The search language is English. All non-English titles are translated.
Special features
- keywording with Emtree, a hierarchical term system like MeSH in PubMed, with numerous synonyms and a focus on drugs and medical devices
- about 3000 journals only in Embase (compared to PubMed), "...we give special attention to journals from outside main publishing areas (notably North America and Western Europe)".
- meeting/conference abstracts and clinical trials from ClinicalTrials.gov are also indexed
- display of the number of hits before submitting the search (Quick and PICO search)
Search options
- General
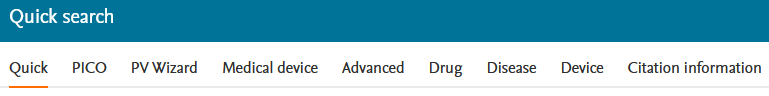
The Quick search mask and Broad search are the standard, combining Emtree terms with analogue text word search in all fields.
The autocomplete function suggests terms from Emtree.
Search strings are possible with OR operator, brackets and wildcards/truncation, e.g. term1 (term2 OR term3*). Phrases (exact word order) can be searched for with single or double inverted commas ("term term*" or 'term term*').
- Wildcard/truncation: * for 0-n characters, ? for 1 character, $ for 0-1 characters centre/right, enter at least 2 characters before.
- Spacing operator: NEAR/n for max. n words away, any order; NEXT/n for specified order.
- Quick search
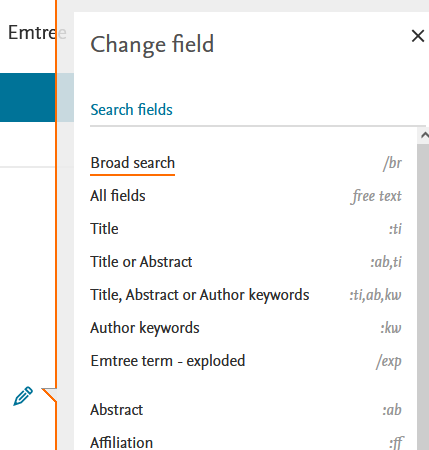
The search fields can be changed with the pencil icon.
For the search below, search aspects were combined via "Add field" (AND search).
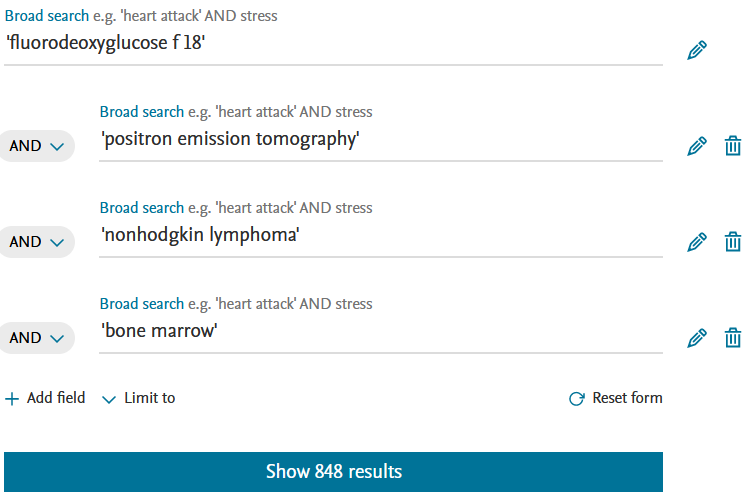
- PICO
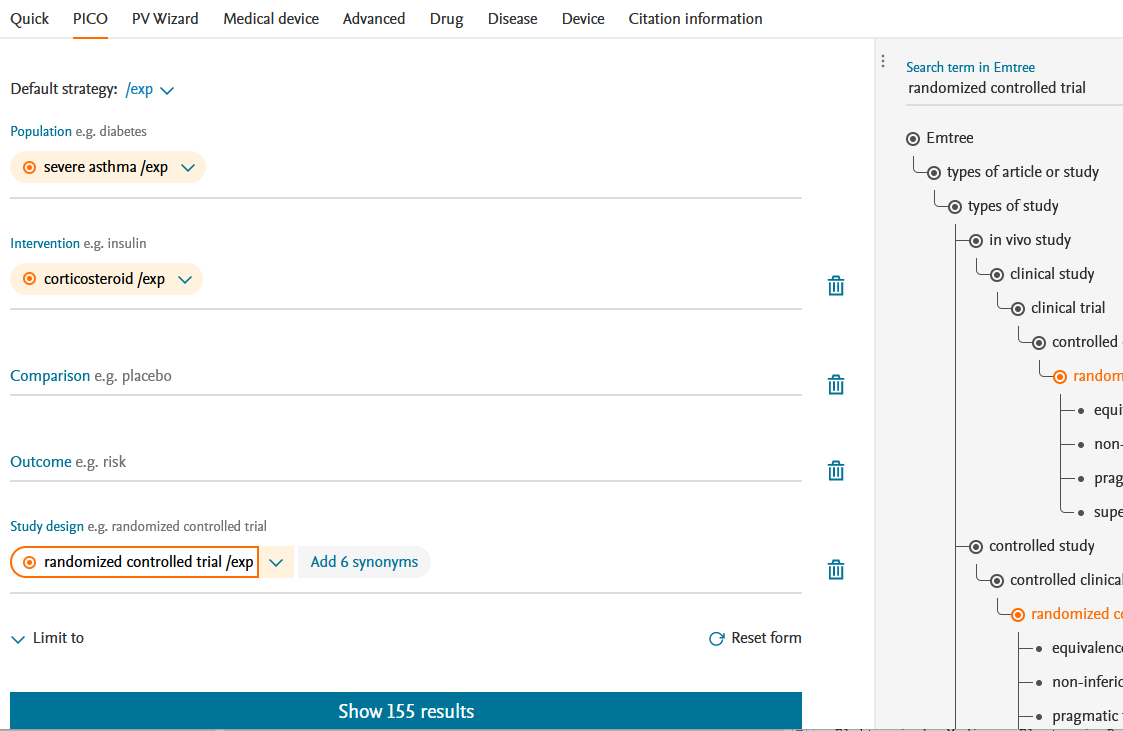
In the PICO search, the search field is already divided into Population (or Patient/Problem), Intervention, Comparison, Outcome and additionally Study design. The automatic emtree search (display of the tree or trees on the right) can be supplemented with synonyms by mouse click, which are then also displayed on the right.
ATTENTION: each click in the tree is transferred to the search field, but can also be deleted via arrow > "Remove term".
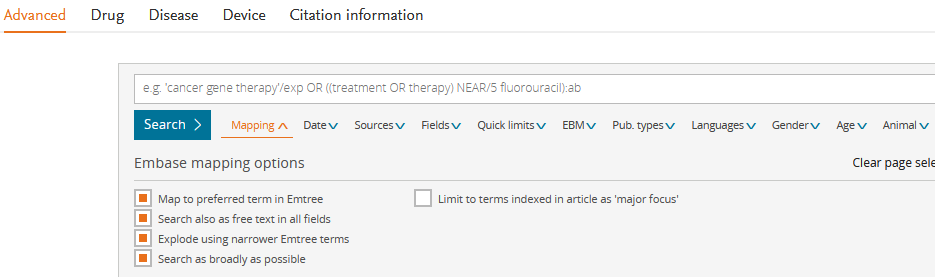
- Advanced search mask
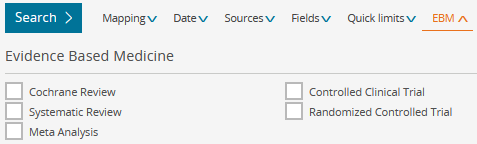
In addition to the mapping ("Search as broadly as possible" activates/deactivates all 4 points, for Broad search see tab General), further expandable filters are displayed. EBM includes the study types "Systematic Review" and "Randomised Controlled Trial", see screenshot.
There is only one search slot.
- Drug, Disease, Device
Like the Advanced search mask, but with subheadings filter.
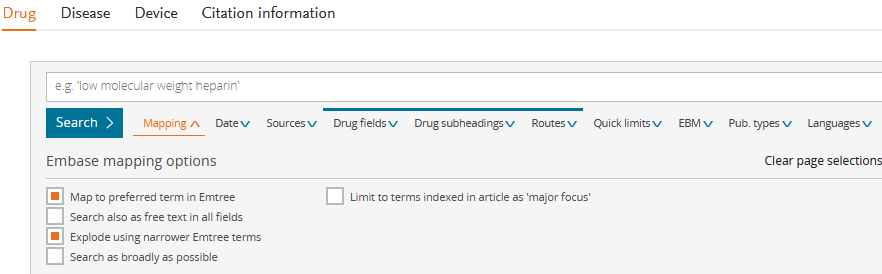
Filter
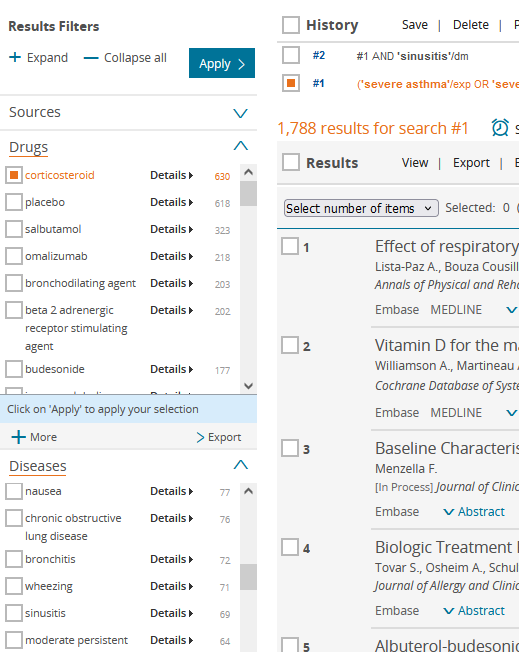
On the results page on the left, numerous filters are displayed, which can be applied after selection with "Apply". For Drugs/Diseases/Devices, subheadings are hidden under Details (see screenshot).
In "Publication types", Conference abstracts can be selected ("Apply") and then adjusted in the search line (or the history via "Edit") to e.g. #1 NOT 'conference abstract'/it (NOT instead of AND).
Result display and export
- Display
The sorting of the hit list can be adjusted and abtracts can be displayed via Show all abstracts. The records per page can only be changed at the bottom.
Each hit leads to the detailed display via the linked title, see screenshot.
If the original language of the article is not English, Translated title Show original is displayed at the top and Language of article at the bottom.
The author addresses can be clicked below the author name.
Further down the emtree terms are shown, divided into Drug/Disease/Device and Other terms, main aspects are in bold.
Below this is further article information.
The icon bar on the right-hand side can be used to export individual hits or to call up our "Check full text" service via the "UB Heidelberg available?" button.

- Save and Clipboard (Watch list)
Hit lists and individual hits
Hit lists and individual hits can be exported in RIS format after selection via Export, which can then be imported with literature management programmes such as EndNote or opened directly.
You must be logged in to use the email function.
Clipboard (watch list)
You can add hit lists or individual hits to the clipboard after selection and save them after login.
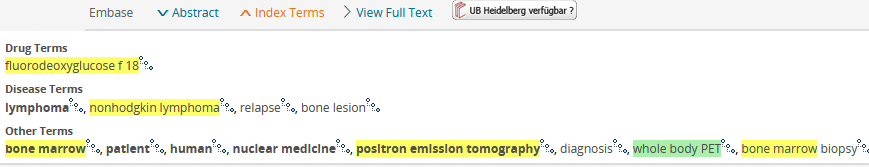
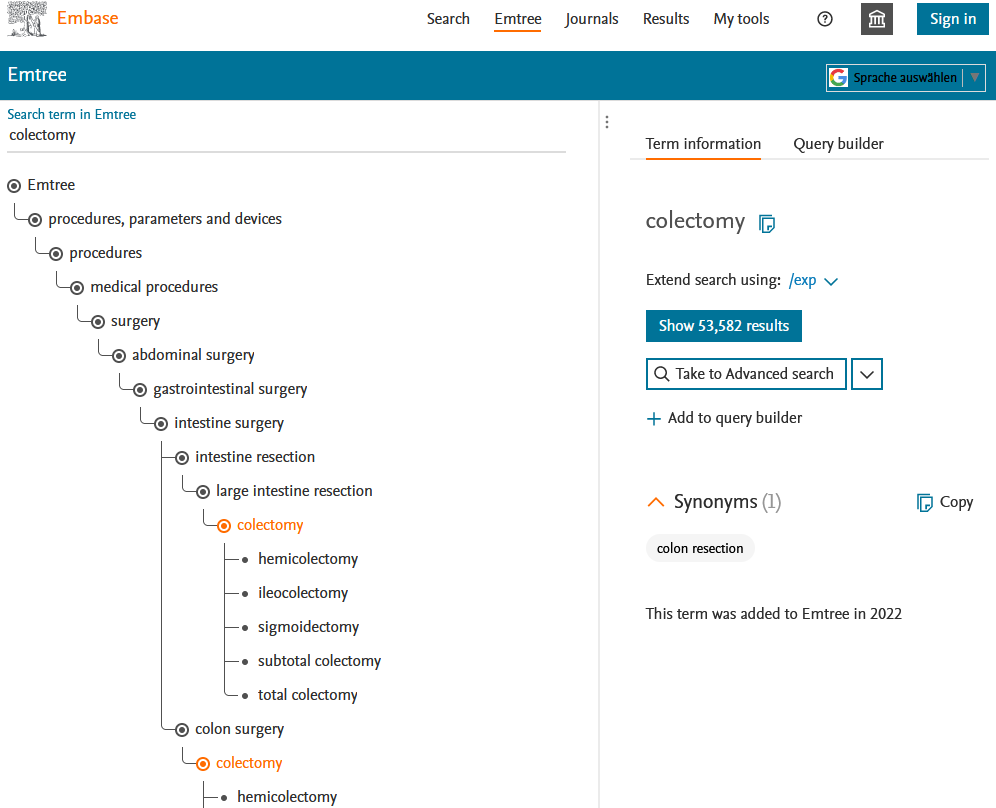
Emtree
By default, English-language keywords (Emtree terms) are displayed via autocomplete for selection for the search. Most literature references are indexed manually with machine support (see here).
- Emtree in hit list and detail view
Emtree terms can already be expanded in the hit list as "Index Terms", see screenshot. The search terms are highlighted in yellow, bold means major focus, green is a keyword in the tree below (Exploded from ...), the three connected dots behind each term lead to the emtree view.
The view in the detail display is similar.
- Emtree (menu)
Using Emtree in the menu bar, you can search specifically for these terms, which are laid out here as a tree structure.
When entered, terms are suggested, which are then displayed on the left in one or more trees.
On the right, the search is preset with /exp (explosion), which means that the search also includes any existing terms below in the tree (narrower or children terms) - this can be changed to e.g. Explosion and major focus, i.e. to main aspect and thus much narrower.
You can also transfer the search term to the Advanced/Drug/Device/Disease search, or park it in the query builder to connect further search terms to it.
Note: there are usually no scope notes that explain the term.
Account and email alerts
After registration/login, you have the following options, which are saved in the "My tools" area:
- Save clipboards (watch lists)
- Click on "Set email alert" on the results page and make the settings; you will then be notified of new hits.
- Save the selected search strategy on the Results page in the "History" section via Save.


Access instructions and "Check full text" service
Database access from outside the faculty network is only possible for members of the faculty with a library identification, see Access options.
Use the "Check full text" service via the button "UB Heidelberg verfügbar?" to call up full texts or order them via the document delivery service.