Sie befinden sich hier
Inhalt

Head of research group on Neuroimaging of
Addictive Behaviour
Central Institute of Mental Health
The Research Group „Neuroimaging of Addictive Behaviour“ investigates the neurobiological underpinnings of addictive behaviour using multimodal imaging. The RG is part of the Department of Addictive Behaviour and Addiction Medicine at the Central Institute of Mental Health.
The research focus is the
- pathogenesis of addiction disorders
- identification of mechanisms that trigger relapse
- identification of neural addiction biomarkers
- influence of genetic variation in addiction initiation and maintenance („Imaging Genetics“)
The projects do not only cover fundamental research, but also serve to improve and evaluate therapeutic interventions. Besides substance-related disorders (mainly alcohol, tobacco, opioid addiction), the RG is focusing on behavioural addictions in cooperation with the RG on internet and media addiction and the RG on pathological gambling.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the imaging method mainly used with a focus on functional MRI, voxel-based morphometry (VBM), diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). Additionally to imaging methods, neuropsychological and psychometric methods and questionnaires are developed and validated to examine addictive behaviour.
Figures
National and international joint research projects
DFG: The addictive potential of the E-cigarette: neurobiological, sociological and epidemiological perspectives; Duration: 2020 – 2023
DFG: TRR 265 “Losing and Regaining Control over Drug Intake: From Trajectories to Mechanisms to Interventions”; Duration: since 2019
- Subproject C01: Modification of the imbalance between goal-directed and habitual behaviour in human addiction (together with Herta Flor)
DFG: "Investigating Neurobiological Mechanisms of Chess as an Add-On Treatment against Alcohol Use Disorder". Duration: 2019 – 2024
DFG: RTG 2350 "Impact of Adverse Childhood Experiences on Psychosocial and Somatic Conditions Across the Lifespan"; Duration: 2018 – 2024
- Subproject B5: Stress sensitivity, emotion processing and cue-reactivity in substance-related disorders: the influence of ACE
Selected publications
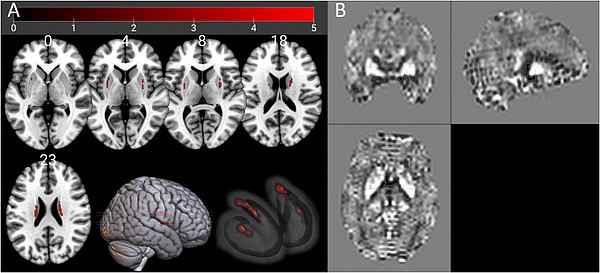
- Association between iron accumulation in the dorsal striatum and compulsive drinking in alcohol use disorder.
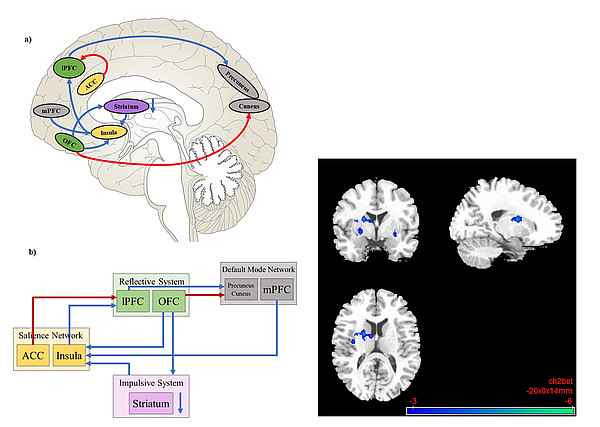
Tan H, Hubertus S, Thomas S, Lee A M, Gerhardt S, Gerchen M F, Sommer W H, Kiefer F, Schad L and Vollstädt-Klein S (2023) Psychopharmacology 240:249-257. doi:10.1007/s00213-022-06301-7 - The effects of nalmefene on the impulsive and reflective system in alcohol use disorder: A resting-state fMRI study.
Grundinger N, Gerhardt S, Karl D, Mann K, Kiefer F, Vollstädt-Klein S (2022). Psychopharmacology. 239(8):2471-2489. doi:10.1007/s00213-022-06137-1 - A History of Childhood Maltreatment Has Substance- and Sex-Specific Effects on Craving During Treatment for Substance Use Disorders.
Gerhardt S, Eidenmueller K, Hoffmann S, Bekier NK, Bach P, Hermann D, Koopmann A, Sommer WH, Kiefer F, Vollstädt-Klein S (2022). Front Psychiatry. 13:866019. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2022.866019 - Investigation of brain functional connectivity to assess cognitive control over cue-processing in Alcohol Use Disorder.
Strosche A, Zhang X, Kirsch M, Hermann D, Ende G, Kiefer F, Vollstädt-Klein S (2020) Addiction Biology. 26(1):e12863. doi:10.1111/adb.12863 - Interaction between behavioral inhibition and neural alcohol cue-reactivity in ADHD and alcohol use disorder.
Vollstädt-Klein S*, Gerhardt S*, Lee A, Strosche A, Sharafi G, Nuriyeva R, Seidt J, Hennig O, Alm B, Hermann D, Sommer W H, Kiefer F, Luderer M and Sobanski E (2020) Psychopharmacology. 237:1691-1707 doi:10.1007/s00213-020-05492-1 *equal contribution - The training game SALIENCE for the therapy of alcohol use disorder.
Vollstädt-Klein S*, Mildner P*, Bumb JM*, Karl D, Ueberle C, Shevchenko Y, Kiefer F, Effelsberg W (2019) Health Informatics Journal. 26(1):499-51. doi:10.1177/1460458219839612 *equal contribution - Oxytocin Reduces Alcohol Cue-Reactivity in Alcohol Dependent Rats and Humans.
Hansson A C, Koopmann A, Uhrig S, Bühler S, Domi E, Kiessling E, Ciccocioppo R, Froemke R C, Grinevich V, Kiefer F, Sommer W H, Vollstädt-Klein S* and Spanagel R* (2018) Neuropsychopharmacology. 43:1235-46. doi:10.1038/npp.2017.257 *equal contribution - Effects of D-cycloserine on extinction of mesolimbic cue-reactivity in alcoholism: A randomized placebo-controlled trial.
Kiefer F, Kirsch M, Bach P, Hoffmann S, Reinhard I, Jorde A, Goltz C v d, Spanagel R, Mann K, Loeber S, Vollstädt-Klein S (2015) Psychopharmacology. 232:2353-2362. doi:10.1007/s00213-015-3882-5 - Development and Validation of the Craving Automated Scale for Alcohol (CAS-A).
Vollstädt-Klein S, Leménager T, Jorde A, Kiefer F and Nakovics H (2015) Alcoholism: Clinical and experimental research. 39:333-342. doi:10.1111/acer.12636 - Validating incentive salience with functional magnetic resonance imaging: association between mesolimbic cue reactivity and attentional bias in alcohol-dependent patients.
Vollstädt-Klein S, Loeber S, Richter A, Kirsch M, Bach P, von der Goltz C, Hermann D, Mann K, Kiefer F (2012) Addiction Biology. 17:807-816. doi:10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00352.x
Photo Credits: #1 Central Institute of Mental Health
Kontextspalte
Contact
Central Institute of Mental Health
J 5
68159 Mannheim
Phone + 49 621 1703-3912
Fax + 49 621 1703-3505
s.vollstaedt-klein@zi-mannheim.de