Sie befinden sich hier
Inhalt

Graduate: Mahdieh Yarmohammadi
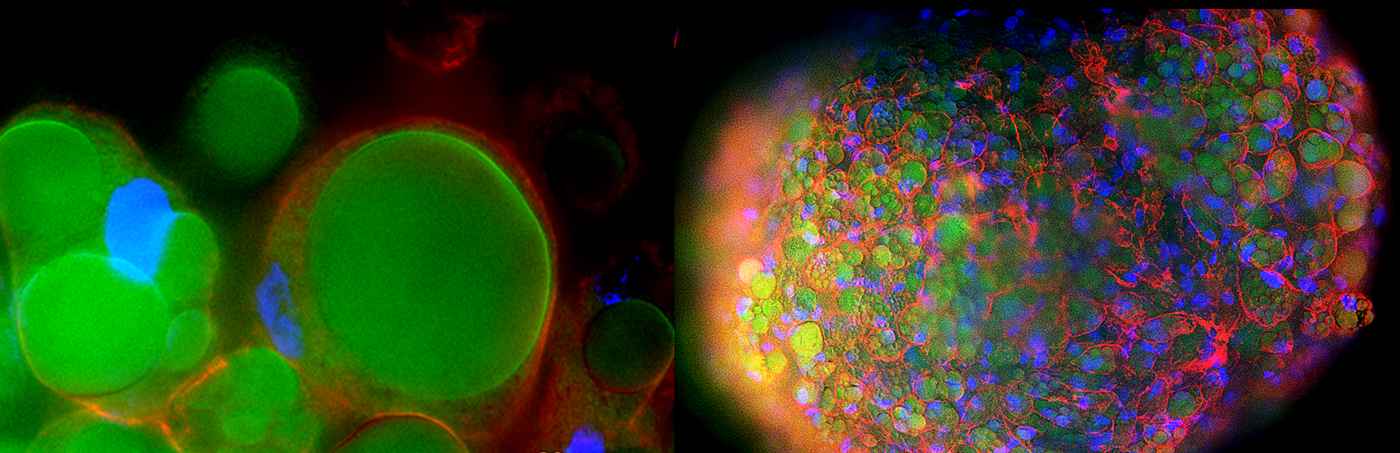
My work is focused on 3D human adipose tissue model containing endothelial and immune cells for disease modeling. We are also interested in investigating Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the treatment of metabolic syndromes including obesity.

Supervisor: Prof. apl. Dr. rer. nat. Karen Bieback
karen.bieback@medma.uni-heidelberg.de
Institute of Transfusion Medicine and Immunology, Medical Faculty Mannheim, Heidelberg University
www.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/transfusionsmedizin-und-immunologie/forschung/ag-bieback/
www.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/mi3/
www.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/core-facilities/flowcore/